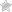Page Contents
- 1 2.7L ENGINE COMPARTMENT
- 2 3.5L ENGINE COMPARTMENT
- 3 5.7L ENGINE COMPARTMENT
- 4 ONBOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM — OBD II
- 5 EMISSIONS INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROGRAMS
- 6 REPLACEMENT PARTS
- 7 DEALER SERVICE
- 8 MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
- 8.1 Engine Oil
- 8.2 Engine Oil Filter
- 8.3 Drive Belts — Check Condition and Tension
- 8.4 Spark Plugs
- 8.5 Engine Air Cleaner Filter
- 8.6 Fuel Filter
- 8.7 Catalytic Converter
- 8.8 Maintenance-Free Battery
- 8.9 Air Conditioner Maintenance
- 8.10 A/C Air Filter — If Equipped
- 8.11 Power Steering — Fluid Check
- 8.12 Front & Rear Suspension Ball Joints
- 8.13 Steering Linkage
- 8.14 Body Lubrication
- 8.15 Windshield Wiper Blades
- 8.16 Windshield Washers/Headlight Washers — If Equipped
- 8.17 Exhaust System
- 8.18 Cooling System
- 8.19 Hoses and Vacuum/Vapor Harnesses
- 8.20 Fuel System
- 8.21 Brake System
- 8.22 Automatic Transmission
- 8.23 All Wheel Drive (AWD) — If Equipped
- 8.24 Front and Rear Wheel Bearings
- 8.25 Appearance Care and Protection from Corrosion
- 8.26 Cleaning the Center Console Cup Holders — 300 Models
- 8.27 Cleaning the Center Console Cup Holders — 300C and 300 Touring Models
- 9 FUSES (POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTERS)
- 10 VEHICLE STORAGE
- 11 REPLACEMENT BULBS
- 12 BULB REPLACEMENT
- 12.1 Low Beam Headlight, High Beam Headlight, Park/Turn Light, Inner Park Light, and Outer Park Light – 300 Models
- 12.2 Low Beam Headlight, High Beam Headlight, and Park/Turn Light – 300C
- 12.3 Backup Light, Side Marker Light, and Tail/Stop Turn Light — 300 Models
- 12.4 Tail/Stop, Tail, Turn Signal Light, and Backup Light — 300C Models
- 13 FLUIDS AND CAPACITIES
- 14 FLUIDS, LUBRICANTS, AND GENUINE PARTS
2.7L ENGINE COMPARTMENT

3.5L ENGINE COMPARTMENT

5.7L ENGINE COMPARTMENT

ONBOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM — OBD II
Your vehicle is equipped with a sophisticated onboard diagnostic system called OBD II. This system monitors the performance of the emissions, engine, and automatic transmission control systems. When these systems are operating properly, your vehicle will provide excellent performance and fuel economy, as well as engine emissions well within current government regulations. If any of these systems require service, the OBD II system will turn on the “Malfunction Indicator Light.” It will also store diagnostic codes and other information to assist your service technician in making repairs. Although your vehicle will usually be drivable and not need towing, see your dealer for service as soon as possible.
CAUTION!
Prolonged driving with the “Malfunction Indicator Light” on could cause further damage to the emission control system. It could also affect fuel economy and driveability. The vehicle must be serviced before any emissions tests can be performed. If the “Malfunction Indicator Light” is flashing while the engine is running, severe catalytic converter damage and power loss will soon occur. Immediate service is required.
Loose Fuel Filler Cap
If the vehicle diagnostic system determines that the fuel filler cap is loose, improperly installed, or damaged, a “Check Gascap” message will display in the Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) — if equipped. If this occurs, tighten the fuel filler cap properly and press the odometer reset button to turn off the message. If the problem continues, the message will appear the next time the vehicle is started.
A loose, improperly installed, or damaged fuel filler cap may also turn on the Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL).
EMISSIONS INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROGRAMS
In some localities, it may be a legal requirement to pass an inspection of your vehicle’s emissions control system. Failure to pass could prevent vehicle registration.

is functioning and is not on when the engine is running, and that the OBD (On Board Diagnostic) system is ready for testing.
Normally, the OBD system will be ready. The OBD system may not be ready if your vehicle was recently serviced, if you recently had a dead battery, or a battery replacement. If the OBD system should be determined not ready for the I/M test, your vehicle may fail the test. Your vehicle has a simple ignition key actuated test, which you can use prior to going to the test station. To check if your vehicle’s OBD system is ready, you must do the following:
1. Insert your ignition key into the ignition switch.
2. Turn the ignition to the ON position, but do not crank or start the engine.
3. If you crank or start the engine, you will have to start this test over.
4. As soon as you turn your key to the ON position, you will see your MIL symbol come on as part of a normal bulb check.
5. Approximately 15 seconds later, one of two things will happen:
a. The MIL will flash for about 10 seconds and then return to being fully illuminated until you turn off the ignition key or start the engine. This means that your vehicle’s OBD system is not ready and you should not proceed to the I/M station.
b. The MIL will not flash at all and will remain fully illuminated until you turn off the ignition key or start the engine. This means that your vehicle’s OBD system is ready and you can proceed to the I/M station.
If your OBD system is not ready, you should see your authorized dealer or repair facility. If your vehicle was recently serviced or had a battery failure or replacement, you may need to do nothing more than drive your vehicle as you normally would in order for your OBD system to update. A recheck with the above test routine may then indicate that the system is now ready. Regardless of whether your vehicle’s OBD system is ready or not ready, if the MIL symbol is illuminated during normal vehicle operation, you should have your vehicle serviced before going to the I/M station. The I/M station can fail your vehicle because the MIL symbol is on with the engine running.
REPLACEMENT PARTS
Use of genuine Mopar parts for normal/scheduled maintenance and repairs is highly recommended to insure the designed performance. Damage or failures caused by the use of non-Mopar parts for maintenance and repairs will not be covered by the manufacturer’s warranty.
DEALER SERVICE
Your dealer has the qualified service personnel, special tools, and equipment to perform all service operations in an expert manner. Service Manuals are available which include detailed service information for your vehicle. Refer to these manuals before attempting any procedure yourself.
NOTE: Intentional tampering with emissions control systems can result in civil penalties being assessed against you.
WARNING!
You can be badly injured working on or around a motor vehicle. Only do service work for which you have the knowledge and the proper equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a competent mechanic.
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
The pages that follow contain the required maintenance services determined by the engineers who designed your vehicle. Besides the maintenance items for which there are fixed maintenance intervals, there are other items that should operate satisfactorily without periodic maintenance. However, if a malfunction of these items does occur, it could adversely affect the engine or vehicle performance. These items should be inspected if a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Engine Oil
Checking Oil Level — 2.7L, 3.5L Engines
To assure proper engine lubrication, the engine oil must be maintained at the correct level. Check the oil level at regular intervals, such as every fuel stop. The best time to check the engine oil level is about 5 minutes after a fully warmed engine is shut off or before starting the engine after it has sat overnight. Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level readings. Maintain the oil level between the MIN and MAX markings on the dipstick. Adding 1.0 quart (1.0L) of oil when the reading is at the MIN mark will result in a MAX reading on these engines.

CAUTION!
Overfilling or underfilling will cause oil aeration or loss of oil pressure. This could damage your engine.
Checking Oil Level — 5.7L Engine
To assure proper engine lubrication, the engine oil must be maintained at the correct level. Check the oil level at regular intervals, such as every fuel stop. The best time to check the engine oil level is about 5 minutes after a fully warmed engine is shut off or before starting the engine after it has sat overnight. Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level readings. Maintain the oil level in the “SAFE” range. Adding 1.0 quart (1.0L) of oil when the reading is at the bottom of the “SAFE” range will result in an oil level at the top of the “SAFE” range on these engines.
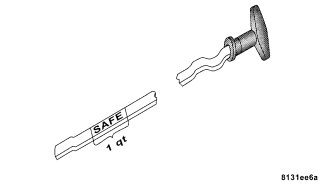
CAUTION!
Overfilling or underfilling will cause oil aeration or loss of oil pressure. This could damage your engine.
Change Engine Oil
Road conditions and your kind of driving affect the interval at which your oil should be changed. Check the following list to see if any apply to you.
• Day or night temperatures are below 32°F (0°C).
• Stop and Go driving.
• Extensive engine idling.
• Driving in dusty conditions.
• Short trips of less than 10 miles (16 km).
• More than 50% of your driving is at sustained high speeds during hot weather, above 90°F (32°C).
• Trailer towing.
• Taxi, Police, or delivery service (commercial service).
• Off-Road or desert operation.
NOTE: If ANY of these apply to you, then change your engine oil every 3,000 miles (5 000 km) or 3 months, whichever comes first, and follow schedule “B” in the Maintenance Schedules in this manual.
If none of these applies to you, then change your engine oil at every interval shown on schedule A in the Maintenance Schedules in this manual.
NOTE: Under no circumstances should oil change intervals exceed 6,000 miles (10 000 km) or 6 months, whichever comes first.
Engine Oil Selection
For best performance and maximum protection under all types of operating conditions, the manufacture only recommends engine oils that are API certified and meet the requirements of DaimlerChrysler Material Standard MS-6395.
American Petroleum Institute (API) Engine Oil Identification Symbol

Engine Oil Viscosity (SAE Grade) — 2.7L and 5.7L Engines
SAE 5W-20 engine oil is recommended for all operating temperatures. This engine oil improves low temperature starting and vehicle fuel economy. The engine oil filler cap also shows the recommended engine oil viscosity for your engine. For information on engine oil filler cap location, “Engine Compartment” illustration in this section.
NOTE: Vehicles equipped with a 5.7L engine must use SAE 5W-20 oil. Failure to do so may result in improper operation of the Multiple Displacement System (MDS). “Multi Displacement System” under “Starting and Operating” for details. In areas where these grades are not generally available, higher SAE grades may be used. Lubricants that have both an SAE grade number and the API Certification Symbol or ACEA category shown on the container should be used. Lubricants that do not have both the engine oil certification mark and the correct SAE viscosity grade number should not be used.
Engine Oil Viscosity (SAE Grade) — 3.5L
Engine SAE 10W-30 engine oil is preferred for use in 3.5L Engines within the operating temperatures shown in the engine oil viscosity chart. SAE 5W-30 Engine Oil is allowed for use in the 3.5L Engine during cold weather only to improve cold weather starting.

The engine oil filler cap also shows the recommended engine oil viscosity for your engine. For information on engine oil filler cap location, “Engine Compartment” illustration in this section. In areas where these grades are not generally available, higher SAE grades may be used. Lubricants that have both an SAE grade number and the API Certification Symbol or ACEA category shown on the container should be used. Lubricants that do not have both the engine oil certification mark and the correct SAE viscosity grade number should not be used.
Synthetic Engine Oils
You may use synthetic engine oils provided the recommended oil quality requirements are met, and the recommended maintenance intervals for oil and filter changes are followed.
Materials Added to Engine Oil
The manufacturer strongly recommends against the addition of any additives (other than leak detection dyes) to the engine oil. Engine oil is an engineered product and its performance may be impaired by supplemental additives.
Disposing of Used Engine Oil and Oil Filters
Care should be taken in disposing of used engine oil and oil filters from your vehicle. Used oil and oil filters, indiscriminately discarded, can present a problem to the environment. Contact your dealer, service station, or governmental agency for advice on how and where used oil and oil filters can be safely discarded in your area.
Engine Oil Filter
The engine oil filter should be replaced at every engine oil change.
Engine Oil Filter Selection
This manufacturer’s engines have a full-flow type oil filter. Use a filter of this type for replacement. The quality of replacement filters varies considerably. Only high quality filters should be used to assure most efficient service. Mopar Engine Oil Filters are a high quality oil filter and are recommended.
Drive Belts — Check Condition and Tension
Belt tension is controlled by means of an automatic tensioner. Therefore, no belt tension adjustments are required. However, belt and belt tensioner condition should be inspected at the specified intervals and replaced if required. Improper belt tension can cause belt slippage and failure. Low generator belt tension can cause battery failure. At the mileage indicated in the maintenance schedule, inspect belt and belt tensioner condition. Inspect belts for evidence of cuts, cracks, glazing, or frayed cords and replaced if there is indication of damage, which could result in belt failure. Also, check belt routing to make sure there is no interference between the belts and other engine components. See your authorized dealer for service.
Spark Plugs
Spark plugs must fire properly to assure engine performance and emission control. New plugs should be installed at the specified mileage. The entire set should be replaced if there is any malfunction due to a faulty spark plug. Malfunctioning spark plugs can damage the catalytic converter. For proper type of replacement spark plugs, “Vehicle Emission Control Information” label in the engine compartment.
Engine Air Cleaner Filter
For normal driving conditions, inspect and replace the engine air cleaner filter at the intervals shown on Schedule “A.” For vehicles driven frequently in dusty or under severe conditions, inspect and replace the engine air cleaner filter at the intervals shown on Schedule “B.”
WARNING!
The air induction system (air cleaner, hoses, etc) can provide a measure of protection in the case of engine backfire. Do not remove the air induction system (air cleaner, hoses, etc) unless such removal is necessary for repair or maintenance. Make sure that no one is near the engine compartment before starting the vehicle with the air induction system (air cleaner, hoses, etc) removed. Failure to do so can result in serious personal injury.
Fuel Filter
A plugged fuel filter can cause stalling, limit the speed at which a vehicle can be driven or cause hard starting. Should an excessive amount of dirt accumulate in the fuel tank, filter replacement may be necessary. See your local dealer for service.
Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter requires the use of unleaded fuel only. Leaded gasoline will destroy the effectiveness of the catalyst as an emission control device. Under normal operating conditions, the catalytic converter will not require maintenance. However, it is important to keep the engine properly tuned to assure proper catalyst operation and prevent possible catalyst damage.
CAUTION!
Damage to the catalytic converter can result if your vehicle is not kept in proper operating condition. In the event of engine malfunction, particularly involving engine misfire or other apparent loss of performance, have your vehicle serviced promptly. Continued operation of your vehicle with a severe malfunction could cause the converter to overheat, resulting in possible damage to the converter and the vehicle.
NOTE: Intentional tampering with emissions control systems can result in civil penalties being assessed against you.
WARNING!
A hot exhaust system can start a fire if you park over materials that can burn. Such materials might be grass or leaves coming into contact with your exhaust system. Do not park or operate your vehicle in areas where your exhaust system can contact anything that can burn.
In unusual situations involving grossly malfunctioning engine operation, a scorching odor may indicate severe and abnormal catalyst overheating. If this should occur, safely bring the vehicle to a complete stop, shut the engine off, and allow the vehicle to cool. Thereafter, obtain service, including a tune-up to manufacturer’s specifications immediately.
To minimize the possibility of catalyst damage:
• Do not shut off the engine or interrupt the ignition when the transmission is in gear and the vehicle is in motion.
• Do not try to start engine by pushing or towing the vehicle.
• Do not idle the engine with any spark plug wires disconnected or removed, such as when diagnostic testing, or for prolonged periods during very rough idling or malfunctioning operating conditions.
Maintenance-Free Battery
The top of the MAINTENANCE-FREE battery is permanently sealed. You will never have to add water, nor is periodic maintenance required. NOTE: The battery is stored under an access cover in the trunk. Remote battery terminals are located in the engine compartment for jump-starting.

WARNING!
• Battery fluid is a corrosive acid solution and can burn or even blind you. Don’t allow battery fluid to contact your eyes, skin, or clothing. Don’t lean over a battery when attaching clamps. If acid splashes in eyes or on skin, flush the area immediately with large amounts of water.
• Battery gas is flammable and explosive. Keep flame or sparks away from the battery. Don’t use a booster battery or any other booster source with an output greater than 12 volts. Don’t allow cable clamps to touch each other.
• Battery posts, terminals, and related accessories contain lead and lead compounds. Wash hands after handling.
• The battery in this vehicle has a vent hose that should not be disconnected and should only be replaced with a battery of the same type (vented).
CAUTION!
• It is essential when replacing the cables on the battery that the positive cable is attached to the positive post and the negative cable is attached to the negative post. Battery posts are marked positive (+) and negative (-) and identified on the battery case. Cable clamps should be tight on the terminal posts and free of corrosion.
• If a “fast charger” is used while battery is in vehicle, disconnect both vehicle battery cables before connecting the charger to battery. Do not use a “fast charger” to provide starting voltage.
Air Conditioner Maintenance
For best possible performance, your air conditioner should be checked and serviced by an Authorized Dealer at the start of each warm season. This service should include cleaning of the condenser fins and a performance test. Drive belt tension should also be checked at this time.
WARNING!
• Use only refrigerants and compressor lubricants approved by the manufacturer for your air conditioning system. Some unapproved refrigerants are flammable and can explode, injuring you. Other unapproved refrigerants or lubricants can cause the system to fail, requiring costly repairs. Refer to Section 3 of the Warranty Information book for further warranty information.
• The air conditioning system contains refrigerant under high pressure. To avoid risk of personal injury or damage to the system, adding refrigerant or any repair requiring lines to be disconnected should be done by an experienced technician.
Refrigerant Recovery and Recycling
R-134a Air Conditioning Refrigerant is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) that is endorsed by the Environmental Protection Agency and is an ozone-saving product. However, the manufacturer recommends that air conditioning service be performed by dealers or other service facilities using recovery and recycling equipment.
NOTE: Use only manufacturer approved A/C System Sealers, Stop Leak Products, Seal Conditioners, Compressor Oil, and Refrigerants.
A/C Air Filter — If Equipped
The filter is located in the fresh air inlet under the hood, behind a removable panel in the cowl on the passenger side of the vehicle, next to the windshield wipers. When installing a new filter, ensure its proper orientation. To replace the filter remove the access door in the cowl screen by pressing the retaining clips. Slide the lid on the filter adapter forward and down and remove used filter. Install new filter with arrows pointing in the direction of airflow, which is toward the rear of the vehicle (text and arrows on the filter indicate this).
“Maintenance Schedule” in this manual for the recommended air conditioning filter replacement intervals.
Power Steering — Fluid Check
Checking the power steering fluid level at a defined service interval is not required. The fluid should only be checked if a leak is suspected, abnormal noises are apparent, and/or the system is not functioning as anticipated. Coordinate inspection efforts through a certified DaimlerChrysler Dealership.
WARNING!
Fluid level should be checked on a level surface and with the engine off to prevent injury from moving parts and to insure accurate fluid level reading. Do not overfill. Use only manufacturer’s recommended power steering fluid.
If necessary, add fluid to restore to the proper indicated level. With a clean cloth, wipe any spilled fluid from all surfaces. “Fluids, Lubricants, and Genuine Parts” in this section for the correct fluid type.
Front & Rear Suspension Ball Joints
The suspension ball joints should be inspected for external leakage or damage when other maintenance is performed.
Steering Linkage
The tie rod end ball joints should be inspected for external leakage or damage when other maintenance is performed.
Body Lubrication
Locks and all body pivot points, including seat tracks, door hinges, trunk hinges, and hood hinges, should be lubricated periodically to assure quiet, easy operation and to protect against rust and wear. Prior to the application of any lubricant, the parts concerned should be wiped clean to remove dust and grit; after lubricating excess oil and grease should be removed. Particular attention should also be given to hood latching components to insure proper function. When performing other underhood services, the hood latch, release mechanism, and safety catch should be cleaned and lubricated.
The external lock cylinders should be lubricated twice a year, preferably in the fall and spring. Apply a small amount of a high quality lubricant such as Mopar Lock Cylinder Lubricant or equivalent directly into the lock cylinder.
Windshield Wiper Blades
The rubber edges of the wiper blades and the windshield should be cleaned periodically with a sponge or soft cloth and a mild nonabrasive cleaner. This will remove accumulations of salt or road film. Operation of the wipers on dry glass for long periods may cause deterioration of the wiper blades. Always use washer fluid when using the wipers to remove salt or dirt from a dry windshield. Avoid using the wiper blades to remove frost or ice from the windshield. Keep the blade rubber out of contact with petroleum products such as engine oil, gasoline, etc.
Windshield Washers/Headlight Washers — If Equipped
The windshield washer and the headlight washer (if equipped) share the same fluid reservoir. The fluid reservoir is located in the front of the engine compartment on the passenger side of the vehicle. Be sure to check the fluid level in the reservoir at regular intervals. Fill the reservoir with windshield washer solvent (not radiator antifreeze) and operate the system for a few seconds to flush out the residual water. The fluid reservoir will hold nearly 1 gallon (4 liters) of washer fluid when the message “Low Washer Fluid” appears in the Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) — if equipped.
WARNING!
Commercially available windshield washer solvents are flammable. They could ignite and burn you. Care must be exercised when filling or working around the washer solution.
Exhaust System
The best protection against carbon monoxide entry into the vehicle body is a properly maintained engine exhaust system. Whenever a change is noticed in the sound of the exhaust system, when exhaust fumes can be detected inside the vehicle, or when the underside or rear of the vehicle is damaged, have a competent mechanic inspect the complete exhaust system and adjacent body areas for broken, damaged, deteriorated, or mispositioned parts. Open seams or loose connections could permit exhaust fumes to seep into the passenger compartment. In addition, inspect the exhaust system each time the vehicle is raised for lubrication or oil change. Replace as required.
WARNING!
Exhaust gases can injure or kill. They contain carbon monoxide (CO) which is colorless and odorless. Breathing it can make you unconscious and can eventually poison you. To avoid breathing CO, “Exhaust Gas” in the “Safety Tips” section of this manual.
Cooling System
WARNING!
• When working near the radiator cooling fan, disconnect the fan motor lead or turn the ignition switch to the OFF position. The fan is temperature controlled and can start at any time the ignition switch is in the ON position.
• You or others can be badly burned by hot coolant or steam from your radiator. If you see or hear steam coming from under the hood, don’t open the hood until the radiator has had time to cool. Never try to open a cooling system pressure cap when the radiator is hot.
Coolant Checks
Check engine coolant (antifreeze) protection every 12 months (before the onset of freezing weather, where applicable). If coolant is dirty or rusty in appearance, the system should be drained, flushed and refilled with fresh coolant. Check the front of the A/C condenser for any accumulation of bugs, leaves, etc. If dirty, clean by gently spraying water from a garden hose vertically down the face of the condenser. Check the coolant recovery bottle tubing for brittle rubber, cracking, tears, cuts, and tightness of the connection at the bottle and radiator. Inspect the entire system for leaks. With the engine at normal operating temperature (but not running), check the cooling system pressure cap for proper vacuum sealing by draining a small amount of coolant from the radiator drain cock. If the cap is sealing properly, the engine coolant (antifreeze) will begin to drain from the coolant recovery bottle. DO NOT REMOVE THE COOLANT PRESSURE CAP WHEN THE COOLING SYSTEM IS HOT.
Cooling System — Drain, Flush, and Refill
The system should be drained, flushed, and refilled at the intervals shown on the Maintenance Schedule. If the solution is dirty or contains a considerable amount of sediment, clean and flush with a reliable cooling system cleaner. Follow with a thorough rinsing to remove all deposits and chemicals. Properly dispose of old antifreeze solution.
Selection of Coolant
Use only the manufacturer’s recommended coolant. “Fluids, Lubricants, and Genuine Parts” for the correct coolant type.
CAUTION!
• Mixing of coolants other than specified HOAT engine coolants, may result in engine damage and may decrease corrosion protection. If a non-HOAT coolant is introduced into the cooling system in an emergency, it should be replaced with the specified coolant as soon as possible.
• Do not use plain water alone or alcohol-base engine coolant (antifreeze) products. Do not use additional rust inhibitors or antirust products, as they may not be compatible with the radiator engine coolant and may plug the radiator.
• This vehicle has not been designed for use with Propylene Glycol based coolants. Use of Propylene Glycol based coolants is not recommended.
Adding Coolant
Your vehicle has been built with an improved engine coolant that allows extended maintenance intervals. This coolant can be used up to 5 Years or 100,000 miles (160 000 km) before replacement. To prevent reducing this extended maintenance period, it is important that you use the same coolant throughout the life of your vehicle. Please review these recommendations for using Hybrid Organic Additive Technology (HOAT) coolant.
When adding coolant:
• The manufacturer recommends using Mopar Antifreeze/Coolant 5 Year/100,000 Mile Formula HOAT (Hybrid Organic Additive Technology).
• Mix a minimum solution of 50% HOAT engine coolant and distilled water. Use higher concentrations (not to exceed 70%) if temperatures below 34°F (37°C) are anticipated.
• Use only high purity water such as distilled or deionized water when mixing the water/engine coolant solution. The use of lower quality water will reduce the amount of corrosion protection in the engine cooling system.
Please note that it is the owner’s responsibility to maintain the proper level of protection against freezing according to the temperatures occurring in the area where the vehicle is operated.
NOTE: Mixing coolant types will decrease the life of the engine coolant and will require more frequent coolant changes.
Cooling System Pressure Cap
The cap must be fully tightened to prevent loss of coolant, and to insure that coolant will return to the radiator from the coolant recovery bottle. The cap should be inspected and cleaned if there is any accumulation of foreign material on the sealing surfaces.
WARNING!
• The warning words “DO NOT OPEN HOT” on the cooling system pressure cap are a safety precaution. Never add coolant when the engine is overheated. Do not loosen or remove the cap to cool an overheated engine. Heat causes pressure to build up in the cooling system. To prevent scalding or injury, do not remove the pressure cap while the system is hot or under pressure.
• Do not use a pressure cap other than the one specified for your vehicle. Personal injury or engine damage may result.
Disposal of Used Coolant
Used ethylene glycol based engine coolant is a regulated substance requiring proper disposal. Check with your local authorities to determine the disposal rules for your community. To prevent ingestion by animals or children, do not store ethylene glycol based engine coolant in open containers or allow it to remain in puddles on the ground. If ingested by a child, contact a physician immediately. Clean up any ground spills immediately.
Coolant Level
The coolant bottle provides a quick visual method for determining that the coolant level is adequate. With the engine off and cold, the level of the coolant in the bottle should be between the ranges indicated on the bottle. The radiator normally remains completely full, so there is no need to remove the radiator cap unless checking for coolant freeze point or replacing coolant. Advise your service attendant of this. As long as the engine operating temperature is satisfactory, the coolant bottle need only be checked once a month. When additional coolant is needed to maintain the proper level, it should be added to the coolant bottle. Do not overfill.
Points To Remember
NOTE: When the vehicle is stopped after a few miles (kilometers) of operation, you may observe vapor coming from the front of the engine compartment. This is normally a result of moisture from rain, snow, or high
humidity accumulating on the radiator and being vaporized when the thermostat opens, allowing hot coolant to enter the radiator. If an examination of your engine compartment shows no evidence of radiator or hose leaks, the vehicle may be safely driven. The vapor will soon dissipate.
• Do not overfill the coolant recovery bottle.
• Check coolant freeze point in the radiator and in the coolant recovery bottle. If antifreeze needs to be added, contents of coolant recovery bottle must also be protected against freezing.
• If frequent coolant additions are required, or if the level in the coolant recovery bottle does not drop when the engine cools, the cooling system should be pressure tested for leaks.
• Maintain coolant concentration at 50% HOAT engine coolant (minimum) and distilled water for proper corrosion protection of your engine, which contains aluminum components.
• Make sure that the radiator and coolant recovery bottle overflow hoses are not kinked or obstructed.
• Keep the front of the radiator clean. If your vehicle is equipped with air conditioning, keep the front of the condenser clean, also.
• Do not change the thermostat for summer or winter operation. If replacement is ever necessary, install ONLY the correct type thermostat. Other designs may result in unsatisfactory coolant performance, poor gas mileage, and increased emissions.
Hoses and Vacuum/Vapor Harnesses
Inspect surfaces of hoses and nylon tubing for evidence of heat and mechanical damage. Hard or soft spots, brittle rubber, cracking, tears, cuts, abrasions, and excessive swelling indicate deterioration of the rubber. Pay particular attention to those hoses nearest to high heat sources such as the exhaust manifold. Inspect hose routing to be sure hoses do not come in contact with any heat source or moving component, which may cause heat damage or mechanical wear.
Insure nylon tubing in these areas has not melted or collapsed. Inspect all hose connections such as clamps and couplings to make sure they are secure and no leaks are present. Components should be replaced immediately if there is any evidence of wear or damage that could cause failure.
Fuel System
The Electronic Fuel Injection high-pressure fuel system’s hoses and quick connect fittings have unique material characteristics that provide adequate sealing and resist attack by deteriorated gasoline. You are urged to use only the manufacture specified hoses with quick connect fittings, or their equivalent in material and specification, in any fuel system servicing. It is mandatory to replace any damaged hoses or quick connect fittings that have been removed during service. Care should be taken in installing quick connect fittings to insure they are properly installed and fully connected. See your authorized dealer for service.
Brake System
In order to assure brake system performance, all brake system components should be inspected periodically. Suggested service intervals can be found in the “Maintenance Schedule” in this manual.
WARNING!
Riding the brakes can lead to brake failure and possibly an accident. Driving with your foot resting or riding on the brake pedal can result in abnormally high brake temperatures, excessive lining wear, and possible brake damage. You wouldn’t have your full braking capacity in an emergency.
Brake and Power Steering Hoses
When the vehicle is serviced for scheduled maintenance, inspect surface of hoses and nylon tubing for evidence of heat and mechanical damage. Hard and brittle rubber, cracking, tears, cuts, abrasion, and excessive swelling indicate deterioration of the rubber. Particular attention should be made to examining those hose surfaces nearest to high heat sources, such as the exhaust manifold.
Insure nylon tubing in these areas has not melted or collapsed. Inspect all hose connections such as clamps and couplings to make sure they are secure and no leaks are present.
NOTE:
• Often, fluid such as oil, power steering fluid, and brake fluid are used during assembly plant operations to facilitate the assembly of hoses to couplings. Therefore, oil wetness at the hose-coupling area is not necessarily an indication of leakage. Actual dripping of hot fluid when systems are under pressure (during vehicle operation), should be noted before a hose is replaced based on leakage.
• Inspect the brake hoses whenever the brake system is serviced and at every engine oil change. Inspect hydraulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing, or worn spots. If there is any evidence of cracking, scuffing, or worn spots, the hose should be replaced immediately! Eventual deterioration of the hose can take place resulting in a possibility of a burst failure.
WARNING!
Worn brake hoses can burst and cause brake failure. You could have an accident. If you see any signs of cracking, scuffing, or worn spots, have the brake hoses replaced immediately.
Master Cylinder – Brake Fluid Level Check
Check the fluid level in the master cylinder immediately if the brake system warning light indicates system failure. Check the fluid level in the master cylinder when performing underhood services. Clean the top of the master cylinder area before removing the cap. Add fluid to bring the level up to the top of the “FULL” mark on the side of the master cylinder reservoir. Overfilling of fluid is not recommended because it may cause leaking in the system.
Add enough fluid to bring the level up to the requirements described on the brake fluid reservoir. With disc brakes, fluid level can be expected to fall as the brake pads wear. However, low fluid level may be caused by a leak and a checkup may be needed. Use only manufacturer’s recommended brake fluid. “Fluids, Lubricants, and Genuine Parts” for the correct fluid type.
WARNING!
• Overfilling the brake fluid reservoir can result in spilling brake fluid on hot engine parts and the brake fluid catching fire.
• Use of a brake fluid that has a lower initial boiling point than the recommended MOPAR DOT 3 product or a brake fluid that is unidentified as to FMVSS specification may result in sudden brake failure during hard prolonged braking. You could have an accident.
Use only brake fluid that has been in a tightly closed container to avoid contamination from foreign matter or moisture.
CAUTION!
Do not allow petroleum base fluid to contaminate the brake fluid, all brake seal components could be damaged causing partial or complete brake failure.
Automatic Transmission
Fluid Level Check
Regular automatic transmission fluid level checks are not required. For this reason, the dipstick is omitted. If you notice fluid loss or gear shift malfunction, have your authorized dealer check the transmission fluid level.
CAUTION!
• Using a transmission fluid other than the manufacturer’s recommended fluid may cause deterioration in transmission shift quality and/or torque converter shudder. Using a transmission fluid other than that recommended by the manufacturer will result in more frequent fluid and filter changes. “Fluids, Lubricants, and Genuine Parts” for the correct fluid type.
• The fluid level is preset at the factory and it does not require adjustment under normal operating conditions. If a transmission fluid leak occurs, visit your authorized dealer immediately. Severe damage to the transmission may occur. Your authorized dealer has the proper tools to adjust the fluid level accurately.
Fluid and Filter Changes
Automatic transmission fluid and filter should be changed as follows: Normal Usage — No change necessary Severe Usage (fluid and filter) — Maintenance Schedule “B”
Severe Usage is defined as:
• Police, taxi, limousine, commercial type operation, or trailer towing where the vehicle is driven regularly for more than 45 minutes of continuous operation. If the transmission is disassembled for any reason, the fluid and filter should be changed.
Special Additives
Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF) is an engineered product and its performance may be impaired by supplemental additives. Therefore, do not add any fluid additives to the transmission. The only exception to this policy is the use of special dyes to aid in detecting fluid leaks. In addition, avoid using transmission sealers as they may adversely affect seals.
All Wheel Drive (AWD) — If Equipped
The all wheel drive system consists of a Transfer Case and Front Differential. The exterior surface of these components should be inspected for evidence of fluid leaks. Confirmed leaks should be repaired as soon as possible. The transfer case fluid inspection plug is located in the middle of the rear housing. To inspect the transfer case fluid level, remove the inspection plug. The fluid level should be even with the bottom of the hole. The transfer case fill plug is located on the rear housing near the output shaft. The front differential fill plug is located on the outer cover near the halfshaft attachment. To inspect the differential fluid level, remove the fill plug. The fluid level should be even with or slightly below the bottom of the hole.
Fluid Changes
The fluid should be changed as follows:


Severe Usage is defined as:
1. More than 50% of vehicle operation in stop and go traffic where vehicle is driven regularly for more than 45 minutes of continuous operation, such as in heavy city or in construction zone traffic.
2. Police, taxi, limousine, commercial type operation, or trailer towing where the vehicle driven regularly for more than 45 minutes of continuous operation.
Front and Rear Wheel Bearings
Front and rear wheel bearings are permanently sealed. No regular maintenance is required for these components.
Appearance Care and Protection from Corrosion
Protection of Body and Paint from Corrosion
Vehicle body care requirements vary according to geographic locations and usage. Chemicals that make roads passable in snow and ice, and chemicals that are sprayed on trees and road surfaces during other seasons, are highly corrosive to the metal in your vehicle. Outside parking, which exposes your vehicle to airborne contaminants, road surfaces on which the vehicle is operated, extreme hot or cold weather and other extreme conditions will have an adverse effect on paint, metal trim, and underbody protection. The following maintenance recommendations will enable you to obtain maximum benefit from the corrosion resistance built into your vehicle.
What Causes Corrosion?
Corrosion is the result of deterioration or removal of paint and protective coatings from your vehicle. The most common causes are:
• Road salt, dirt, and moisture accumulation.
• Stone and gravel impact. • Insects, tree sap, and tar.
• Salt in the air near seacoast localities.
• Atmospheric fallout/industrial pollutants.
Washing
• Wash your vehicle regularly. Always wash your vehicle in the shade using Mopar Car Wash or a mild car wash soap, and rinse the panels completely with clear water.
• If insects, tar, or other similar deposits have accumulated on your vehicle, use Mopar Super Kleen Bug and Tar Remover to remove.
• Use Mopar Cleaner Wax to remove road film, stains and to protect your paint finish. Take care never to scratch the paint.
• Avoid using abrasive compounds and power buffing that may diminish the gloss or thin out the paint finish.
CAUTION!
Do not use abrasive or strong cleaning materials such as steel wool or scouring powder, which will scratch metal and painted surfaces.
Special Care
• If you drive on salted or dusty roads or if you drive near the ocean, hose off the undercarriage at least once a month.
• It is important that the drain holes in the lower edges of the doors, rocker panels, and trunk be kept clear and open.
• If you detect any stone chips or scratches in the paint, touch them up immediately. The cost of such repairs is considered the responsibility of the owner.
• If your vehicle is damaged due to an accident or similar cause, which destroys the paint and protective coating, have your vehicle repaired as soon as possible. The cost of such repairs is considered the responsibility of the owner.
• If you carry special cargo such as chemicals, fertilizers, de-icer salt, etc., be sure that such materials are well packaged and sealed.
• If a lot of driving is done on gravel roads, consider mud or stone shields behind each wheel.
• Use Mopar touch up paint or equivalent on scratches as soon as possible. Your dealer has touch up paint to match the color of your vehicle.
Wheel and Wheel Trim Care
All wheels and wheel trim, especially aluminum and chrome plated wheels should be cleaned regularly with a mild soap and water to prevent corrosion. To remove heavy soil and/or excessive brake dust, use Mopar Wheel Cleaner (05066247AB) or equivalent or select a nonabrasive, non-acidic cleaner. Do not use scouring pads, steel wool, a bristle brush, or metal polishes. Only Moparor equivalent is recommended. Do not use oven cleaner. Avoid automatic car washes that use acidic solutions or harsh brushes that may damage the wheels’ protective finish.
Interior Care
Use Mopar Fabric Cleaner or equivalent to clean fabric upholstery and Mopar Carpet Cleaner for carpeting. Interior Trim should be cleaned starting with a damp cloth, or Mopar Satin Select. Do not use harsh cleaners or Armorall. Use Mopar Total Clean to clean vinyl upholstery. Mopar Total Clean is specifically recommended for leather upholstery. Your leather upholstery can be best preserved by regular cleaning with a damp soft cloth. Small particles of dirt can act as an abrasive and damage the leather upholstery and should be removed promptly with a damp cloth. Stubborn soils can be removed easily with a soft cloth and Mopar Total Clean or equivalent. Care should be taken to avoid soaking your leather upholstery with any liquid. Please do not use polishes, oils, cleaning fluids, solvents, detergents, or ammonia-based cleaners to clean your leather upholstery. Application of a leather conditioner is not required to maintain the original condition.
WARNING!
Do not use volatile solvents for cleaning purposes. Many are potentially flammable, and if used in closed areas they may cause respiratory harm.
Cleaning Headlights
Your vehicle has plastic headlights that are lighter and less susceptible to stone breakage than glass headlights. Plastic is not as scratch resistant as glass and therefore different lens cleaning procedures must be followed. To minimize the possibility of scratching the lenses and reducing light output, avoid wiping with a dry cloth. To remove road dirt, wash with a mild soap solution followed by rinsing. Do not use abrasive cleaning components, solvents, steel wool or other aggressive material to clean the lenses.
Glass Surfaces
All glass surfaces should be cleaned on a regular basis with Mopar Glass Cleaner or any commercial household-type glass cleaner. Never use an abrasive type
cleaner. Use caution when cleaning the inside rear window equipped with electric defrosters or the right rear quarter window equipped with the radio antenna. Do not use scrapers or other sharp instruments, which may scratch the elements. When cleaning the rear view mirror, spray cleaner on the towel or rag that you are using. Do not spray cleaner directly on the mirror.
Cleaning Plastic Instrument Cluster Lenses
The lenses in front of the instruments in this vehicle are molded in clear plastic. When cleaning the lenses, care must be taken to avoid scratching the plastic
. 1. Clean with a wet soft rag or micro-fiber towel. A mild soap solution may be used, but do not use high alcohol content or abrasive cleaners. If soap is used, wipe clean with a clean damp rag.
2. Dry with a soft tissue.
Seat Belt Maintenance
Do not bleach, dye, or clean the belts with chemical solvents or abrasive cleaners. This will weaken the fabric. Sun damage can also weaken the fabric. If the belts need cleaning, use Mopar Total Clean, a mild soap solution, or lukewarm water. Do not remove the belts from the vehicle to wash them. Replace the belts if they appear frayed or worn or if the buckles do not work properly.
Cleaning the Center Console Cup Holders — 300 Models
Perform the following steps to clean the center console cup holders:
• Grab the center of the rubber portion of the cup holder firmly and lift upward to remove.
• Soak the rubber cup holder liner in a mixture of medium hot tap water and one teaspoon of mild liquid dish soap. Let soak for approximately one hour.
• After one hour pull the liner from the water and dip it back into the water about six times. This will loosen any remaining debris.
• Rinse the liner thoroughly under warm running water. Shake the excess water from the liner and dry the outer surfaces with a clean soft cloth.
• Carefully tuck the front, followed by the rear, then side edges of the cup holder into the center console.
Cleaning the Center Console Cup Holders — 300C and 300 Touring Models
Clean with a damp cloth or towel using a mild detergent with the cup holder in the center console.
NOTE: The cup holder cannot be removed.
FUSES (POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTERS)
Fuses (Front Power Distribution Center)
A power distribution center is located in the engine compartment. This center contains fuses and relays.



CAUTION!
• When installing the Power Distribution Center cover, it is important to ensure the cover is properly positioned and fully latched. Failure to do so may allow water to get into the Power Distribution Center, and possibly result in an electrical system failure.
• When replacing a blown fuse, it is important to use only a fuse having the correct amperage rating. The use of a fuse with a rating other than indicated may result in a dangerous electrical system overload. If a properly rated fuse continues to blow, it indicates a problem in the circuit that must be corrected.
Fuses (Rear Power Distribution Center)
There is also a power distribution center located in the trunk under the spare tire access panel. This center contains fuses and relays.





*Cavities 11, 12, and 13 contain self-resetting fuses (circuit breakers) that are only serviceable by an authorized dealer. The Cluster (without power memory seat), the Driver Seat Switch (with power memory seat), and the Memory Module (if equipped) are fused by the 25 amp circuit breaker in Cavity 11. The Passenger Seat Switch is fused by the 25 amp circuit breaker in Cavity 12. The Door Modules (except base), the Driver Door Lock Switch (base), the Driver Express Power Window Switch (if equipped), and the Passenger Door Lock Switch (base) are fused by the 25 amp circuit breaker in Cavity 13. If you experience temporary or permanent loss of these systems, see your authorized dealer for service.
CAUTION!
• When installing the Power Distribution Center cover, it is important to ensure the cover is properly positioned and fully latched. Failure to do so may allow water to get into the Power Distribution Center, and possibly result in an electrical system failure.
• When replacing a blown fuse, it is important to use only a fuse having the correct amperage rating. The use of a fuse with a rating other than indicated may result in a dangerous electrical system overload. If a properly rated fuse continues to blow, it indicates a problem in the circuit that must be corrected.
VEHICLE STORAGE
If you are leaving your vehicle dormant for more than 21 days, you may want to take steps to protect your battery. You may:
• Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
• Anytime you store your vehicle, or keep it out of service (i.e. vacation) for two weeks or more, run the air conditioning system at idle for about five minutes in the fresh air and high blower setting. This will insure adequate system lubrication to minimize the possibility of compressor damage when the system is started again.
REPLACEMENT BULBS


BULB REPLACEMENT
Low Beam Headlight, High Beam Headlight, Park/Turn Light, Inner Park Light, and Outer Park Light – 300 Models
1. Open the hood.
NOTE: Removal of the air cleaner filter housing may be necessary prior to replacing bulbs in the headlight assembly on the driver side of the vehicle.
2. Twist the appropriate bulb and socket assembly counter-clockwise, and then pull it out of the headlight assembly.
3. Pull the bulb out of the socket assembly.
4. Push the replacement bulb into the socket assembly.
5. Reinstall the bulb and socket assembly into the headlight assembly, and then turn it clockwise.


CAUTION! Do not touch the new bulb with your fingers. Oil contamination will severely shorten bulb life. If the bulb comes in contact with an oily surface, clean the bulb with rubbing alcohol.
Low Beam Headlight, High Beam Headlight, and Park/Turn Light – 300C
High Intensity Discharge Headlights (HID) — If Equipped
The headlights are a type of high voltage discharge tube. High voltage can remain in the circuit even with the headlight switch off and the key removed. Because of this, you should not attempt to service a headlight bulb yourself. If a headlight bulb fails, take your vehicle to an authorized dealer for service.
WARNING! A transient high tension occurs at the bulb sockets of High Intensity Discharge (HID) headlights when the headlight switch is turned ON. It may cause serious electrical shock or electrocution if not serviced properly. See your authorized dealer for service.
NOTE: On vehicles equipped with High Intensity Discharge Headlights (HID), when the headlights are turned on, there is a blue hue to the lights. This diminishes and becomes more white after approximately 10 seconds, as the system charges.
- Open the hood.
NOTE: Removal of the air cleaner filter housing may be necessary prior to replacing bulbs in the headlight assembly on the driver side of the vehicle.
2. Twist the appropriate bulb and socket assembly counter-clockwise, and then pull it out of the headlight assembly.
3. Pull the bulb out of the socket assembly.
4. Push the replacement bulb into the socket assembly.
5. Reinstall the bulb and socket assembly into the headlight assembly, and then turn it clockwise.


CAUTION!
Do not touch the new bulb with your fingers. Oil contamination will severely shorten bulb life. If the bulb comes in contact with an oily surface, clean the bulb with rubbing alcohol.
Backup Light, Side Marker Light, and Tail/Stop Turn Light — 300 Models
1. Open the Trunk.
2. Remove two fasteners from the back of the tail light assembly.

3. Pull back the trunk liner.
4. Remove the remaining fastener from the back of the tail light assembly.
5. Push the electrical connector locking tab to the side.
6. Disconnect the electrical connector.

7. Pull the tail light assembly clear from the vehicle to access the bulbs.
8. Turn the appropriate bulb and socket assembly counter-clockwise to remove it from the tail light assembly.



9. Pull the bulb out of the socket assembly.
10. Push the replacement bulb into the socket assembly.
11. Reinstall the bulb and socket assembly into the tail light assembly, and then turn it clockwise.
12. Reinstall the tail light assembly, fasteners, electrical connector, and trunk liner.
13. Close the trunk.
Tail/Stop, Tail, Turn Signal Light, and Backup Light — 300C Models
1. Open the Trunk.
2. Remove two fasteners from the back of the tail light assembly.

3. Pull back the trunk liner.
4. Remove the remaining fastener from the back of the tail light assembly.
5. Push the electrical connector locking tab to the side.
6. Disconnect the electrical connector.

7. Pull the tail light assembly clear from the vehicle to access the bulbs. Turn bulb sockets counter-clockwise to remove.
8. Turn the appropriate bulb and socket assembly counter-clockwise to remove it from the tail light assembly.



9. Pull the bulb out of the socket assembly.
10. Push the replacement bulb into the socket assembly.
11. Reinstall the bulb and socket assembly into the tail light assembly, and then turn it clockwise.
12. Reinstall the tail light assembly, fasteners, electrical connector, and trunk liner.
13. Close the trunk.
License Light
1. Remove the screws securing the light to the rear fascia.
2. Remove the bulb and socket assembly.
3. Pull the bulb out of the socket assembly.

4. Push the replacement bulb into the socket assembly.
5. Reinstall the bulb and socket assembly.
6. Reattach the light to the rear fascia, and then install the screws.
FLUIDS AND CAPACITIES


FLUIDS, LUBRICANTS, AND GENUINE PARTS
Engine

Chassis